You may have heard the term ‘pre-diabetic’ state, or ‘glucose-intolerance’ but do you know what exactly these terms really mean?
Recently my father did a fasting blood glucose test. The results came as he is in a pre-diabetic state. A person with a pre-diabetic state has high levels of blood glucose. But the levels are not high enough to diagnose as having type 2 diabetes.
They have a higher risk of developing diabetes and other complications like heart diseases.
However, people living with pre-diabetes has a higher chance of developing diabetes and other related complications associated with diabetes.
In a previous post
Most people living with the pre-diabetic state also have other features of metabolic syndrome, such as obesity and high blood cholesterol levels.
How do I know if I am pre-diabetic?
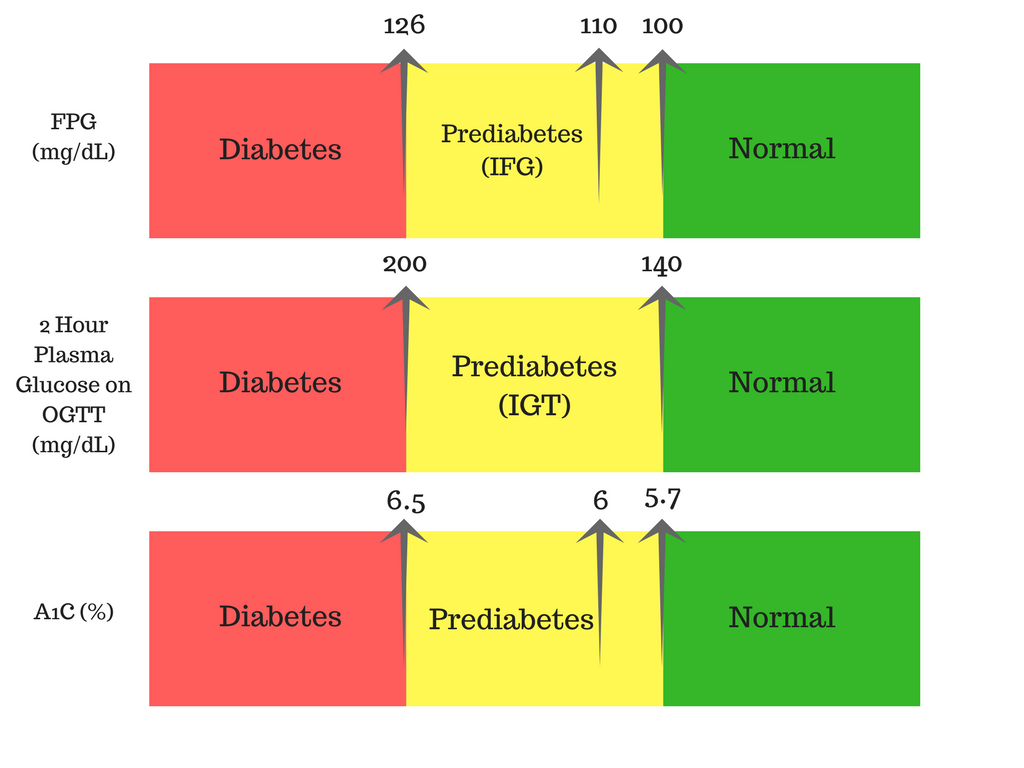
The easiest way to diagnose if you are pre-diabetic is to get a fasting blood glucose level. And if the fasting blood glucose level falls between 100mg/dl to 120mg/dl then you are pre-diabetic.
You can also diagnose whether you have pre-diabetes by doing an HbA1C test or a plasma oral glucose tolerance test.
I will talk about these tests in detail in a later post but I would recommend you doing a fasting blood glucose test because it is least expensive and can also diagnose diabetes.
- WHO (World Health Organization) criteria: fasting plasma glucose level from 6.1 mmol/l (110 mg/dL) to 6.9 mmol/L (125 mg/dL)
- ADA (American Diabetic Association) criteria: fasting plasma glucose level from 5.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL) to 6.9 mmol/L (125 mg/dL)
What should I do if I am pre-diabetic?
The first thing you should do is go and meet your family doctor. He may order you to do some other tests like a lipid profile to determine your blood cholesterol levels.
Depending on the values he may or may not prescribe you medications to lower your cholesterol levels if they are high.
Once you are diagnosed to be pre-diabetic you should adopt healthy dietary habits and do the necessary lifestyle modifications. But this does not mean that people who are already healthy can continue their poor
As we are advising in every post it is important to change your dietary habits irrespective of your health condition.
Be more active

The American heart association advice every adult, whether you are diabetic or not should at least have 30 minutes of moderate exercise at least five days a week. This
If you can go the extra distance you can do a heavy exercise like fast running for 20 minutes at least five days a week.
Lose weight
Most people with pre-diabetes are either obese or overweight. So losing weight is essential if you fall in to these catagories.
Losing at least 5-10 percent of your current body weight can have a huge impact on your blood sugar levels.
Screen for diabetes
If you find yourself to be pre-diabetic it is advisable to followup and do fasting blood sugar levels at least once a year.
Development of diabetes in people with pre-diabetes is not something that is inevitable.
People who are pre-diabetes has 25% risk of developing diabetes within 3 years and 50% chance of developing diabetes in 10 years.
Because these people are can develop diabetes anytime if they continue their current lifestyles. Early intervention can help to control and prevent the development of complications associated with diabetes.





2 Comments
Pingback: Are Artificial Sweeteners Good For People With Diabetes? - Go Grub It
Pingback: We Just Tried Stevia, Should You Try It? Here Our Review. - Go Grub It